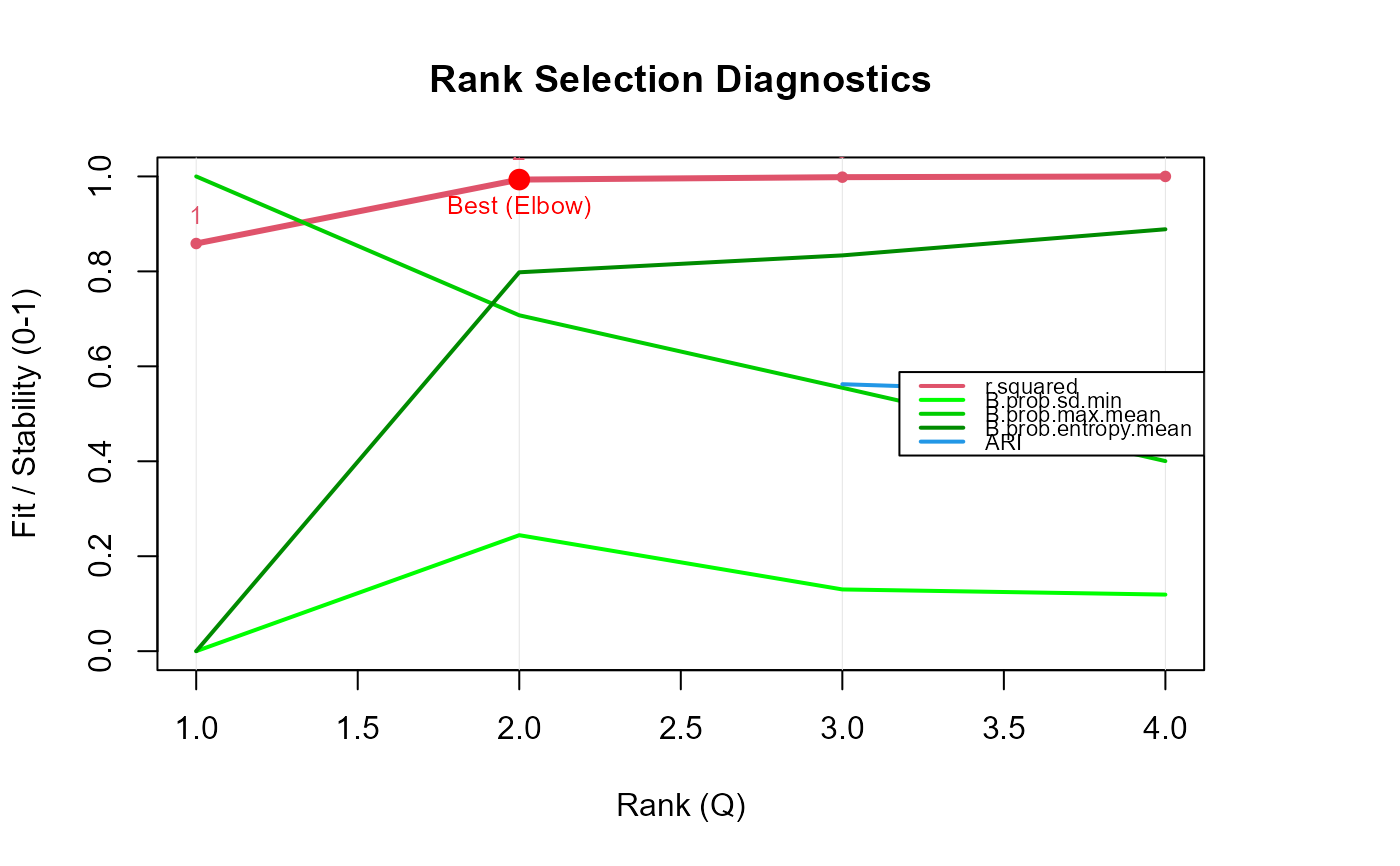
nmfkc.rank provides diagnostic criteria for selecting the rank (\(Q\))
in NMF with kernel covariates. Several model selection measures are computed
(e.g., R-squared, silhouette, CPCC, ARI), and results can be visualized in a plot.
By default (save.time = FALSE), this function also computes the
Element-wise Cross-Validation error (Wold's CV Sigma) using nmfkc.ecv.
The plot explicitly marks the "BEST" rank based on two criteria:
Elbow Method (Red): Based on the curvature of the R-squared values (always computed if Q > 2).
Min RMSE (Blue): Based on the minimum Element-wise CV Sigma (only if
save.time=FALSE).
nmfkc.rank(Y, A = NULL, rank = 1:2, save.time = FALSE, plot = TRUE, ...)Arguments
- Y
Observation matrix.
- A
Covariate matrix. If
NULL, the identity matrix is used.- rank
A vector of candidate ranks to be evaluated.
- save.time
Logical. If
TRUE, skips heavy computations like Element-wise CV. Default isFALSE(computes everything).- plot
Logical. If
TRUE(default), draws a plot of the diagnostic criteria.- ...
Additional arguments passed to
nmfkcandnmfkc.ecv.Q: (Deprecated) Alias forrank.
Value
A list containing:
- rank.best
The estimated optimal rank. Prioritizes ECV minimum if available, otherwise R-squared Elbow.
- criteria
A data frame containing diagnostic metrics for each rank.
References
Brunet, J.P., Tamayo, P., Golub, T.R., Mesirov, J.P. (2004). Metagenes and molecular pattern discovery using matrix factorization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 101, 4164–4169. doi:10.1073/pnas.0308531101 Punera, K., & Ghosh, J. (2008). Consensus-based ensembles of soft clusterings. Applied Artificial Intelligence, 22(7–8), 780–810. doi:10.1080/08839510802170546
Examples
# install.packages("remotes")
# remotes::install_github("ksatohds/nmfkc")
# Example.
library(nmfkc)
Y <- t(iris[,-5])
# Full run (default)
nmfkc.rank(Y, rank=1:4)
#> Y(4,150)~X(4,1)B(1,150)...
#> 0sec
#> Y(4,150)~X(4,2)B(2,150)...
#> 0sec
#> Y(4,150)~X(4,3)B(3,150)...
#> 0sec
#> Y(4,150)~X(4,4)B(4,150)...
#> 0sec
#> Running Element-wise CV (this may take time)...
#> Performing Element-wise CV for Q = 1,2,3,4 (5-fold)...
#> Y(4,150)~X(4,1)B(1,150)...
#> 0sec
#> Y(4,150)~X(4,1)B(1,150)...
#> 0sec
#> Y(4,150)~X(4,1)B(1,150)...
#> 0sec
#> Y(4,150)~X(4,1)B(1,150)...
#> 0sec
#> Y(4,150)~X(4,1)B(1,150)...
#> 0sec
#> Y(4,150)~X(4,2)B(2,150)...
#> 0sec
#> Y(4,150)~X(4,2)B(2,150)...
#> 0sec
#> Y(4,150)~X(4,2)B(2,150)...
#> 0sec
#> Y(4,150)~X(4,2)B(2,150)...
#> 0sec
#> Y(4,150)~X(4,2)B(2,150)...
#> 0sec
#> Y(4,150)~X(4,3)B(3,150)...
#> 0sec
#> Y(4,150)~X(4,3)B(3,150)...
#> 0sec
#> Y(4,150)~X(4,3)B(3,150)...
#> 0sec
#> Y(4,150)~X(4,3)B(3,150)...
#> 0sec
#> Y(4,150)~X(4,3)B(3,150)...
#> 0sec
#> Y(4,150)~X(4,4)B(4,150)...
#> 0sec
#> Y(4,150)~X(4,4)B(4,150)...
#> 0sec
#> Y(4,150)~X(4,4)B(4,150)...
#> 0sec
#> Y(4,150)~X(4,4)B(4,150)...
#> 0sec
#> Y(4,150)~X(4,4)B(4,150)...
#> 0sec
 #> $rank.best
#> [1] 4
#>
#> $criteria
#> rank r.squared ICp AIC BIC B.prob.sd.min
#> 1 1 0.8586795 52.4309 -50.91409 621.8162 0.0000000
#> 2 2 0.9933479 102.3992 -1579.36199 -233.9015 0.2443194
#> 3 3 0.9984511 153.9677 -2147.71982 -129.5291 0.1300233
#> 4 4 0.9999888 202.0625 -4800.29737 -2109.3764 0.1191841
#> B.prob.entropy.mean B.prob.max.mean ARI silhouette CPCC dist.cor
#> 1 0.0000000 1.0000000 NA NA NA 0.9410181
#> 2 0.7980677 0.7075007 NA 0.8692814 0.9264254 0.9746472
#> 3 0.8336790 0.5548794 0.5623250 0.5358708 0.9193853 0.9489567
#> 4 0.8887089 0.4003933 0.5404919 0.3049893 0.8966046 0.9464434
#> sigma.ecv
#> 1 1.1694153
#> 2 0.7997277
#> 3 0.7786008
#> 4 0.7674663
#>
# Fast run (skip ECV)
nmfkc.rank(Y, rank=1:4, save.time=TRUE)
#> Y(4,150)~X(4,1)B(1,150)...
#> 0sec
#> Y(4,150)~X(4,2)B(2,150)...
#> 0sec
#> Y(4,150)~X(4,3)B(3,150)...
#> 0sec
#> Y(4,150)~X(4,4)B(4,150)...
#> 0sec
#> $rank.best
#> [1] 4
#>
#> $criteria
#> rank r.squared ICp AIC BIC B.prob.sd.min
#> 1 1 0.8586795 52.4309 -50.91409 621.8162 0.0000000
#> 2 2 0.9933479 102.3992 -1579.36199 -233.9015 0.2443194
#> 3 3 0.9984511 153.9677 -2147.71982 -129.5291 0.1300233
#> 4 4 0.9999888 202.0625 -4800.29737 -2109.3764 0.1191841
#> B.prob.entropy.mean B.prob.max.mean ARI silhouette CPCC dist.cor
#> 1 0.0000000 1.0000000 NA NA NA 0.9410181
#> 2 0.7980677 0.7075007 NA 0.8692814 0.9264254 0.9746472
#> 3 0.8336790 0.5548794 0.5623250 0.5358708 0.9193853 0.9489567
#> 4 0.8887089 0.4003933 0.5404919 0.3049893 0.8966046 0.9464434
#> sigma.ecv
#> 1 1.1694153
#> 2 0.7997277
#> 3 0.7786008
#> 4 0.7674663
#>
# Fast run (skip ECV)
nmfkc.rank(Y, rank=1:4, save.time=TRUE)
#> Y(4,150)~X(4,1)B(1,150)...
#> 0sec
#> Y(4,150)~X(4,2)B(2,150)...
#> 0sec
#> Y(4,150)~X(4,3)B(3,150)...
#> 0sec
#> Y(4,150)~X(4,4)B(4,150)...
#> 0sec
 #> $rank.best
#> [1] 2
#>
#> $criteria
#> rank r.squared ICp AIC BIC B.prob.sd.min
#> 1 1 0.8586795 52.4309 -50.91409 621.8162 0.0000000
#> 2 2 0.9933479 102.3992 -1579.36199 -233.9015 0.2443194
#> 3 3 0.9984511 153.9677 -2147.71982 -129.5291 0.1300233
#> 4 4 0.9999888 202.0625 -4800.29737 -2109.3764 0.1191841
#> B.prob.entropy.mean B.prob.max.mean ARI silhouette CPCC dist.cor
#> 1 0.0000000 1.0000000 NA NA NA NA
#> 2 0.7980677 0.7075007 NA NA NA NA
#> 3 0.8336790 0.5548794 0.5623250 NA NA NA
#> 4 0.8887089 0.4003933 0.5404919 NA NA NA
#> sigma.ecv
#> 1 NA
#> 2 NA
#> 3 NA
#> 4 NA
#>
#> $rank.best
#> [1] 2
#>
#> $criteria
#> rank r.squared ICp AIC BIC B.prob.sd.min
#> 1 1 0.8586795 52.4309 -50.91409 621.8162 0.0000000
#> 2 2 0.9933479 102.3992 -1579.36199 -233.9015 0.2443194
#> 3 3 0.9984511 153.9677 -2147.71982 -129.5291 0.1300233
#> 4 4 0.9999888 202.0625 -4800.29737 -2109.3764 0.1191841
#> B.prob.entropy.mean B.prob.max.mean ARI silhouette CPCC dist.cor
#> 1 0.0000000 1.0000000 NA NA NA NA
#> 2 0.7980677 0.7075007 NA NA NA NA
#> 3 0.8336790 0.5548794 0.5623250 NA NA NA
#> 4 0.8887089 0.4003933 0.5404919 NA NA NA
#> sigma.ecv
#> 1 NA
#> 2 NA
#> 3 NA
#> 4 NA
#>